Computers have become an essential part of modern life, powering everything from personal tasks to complex business operations. Understanding the different types of computers helps in choosing the right one for specific needs. They range from compact devices like smartphones and laptops to powerful machines such as servers and supercomputers.
Each type serves a unique purpose, offering varying levels of performance, speed, and functionality. Whether for personal use, education, or enterprise solutions, knowing the distinctions between computers ensures efficiency and productivity. Explore the main types to make informed technology decisions.
Read More: Best Computer Courses in Demand for Beginners
What are the types of computers?
Computers are classified by their size, performance, and purpose. Some are compact and portable, like laptops and tablets, while others are large and high-powered, such as mainframes and supercomputers. Each type serves specific needs, from everyday tasks in schools and offices to complex operations in hospitals and industries. Understanding these categories helps in selecting the right computer for work, study, or specialized applications.
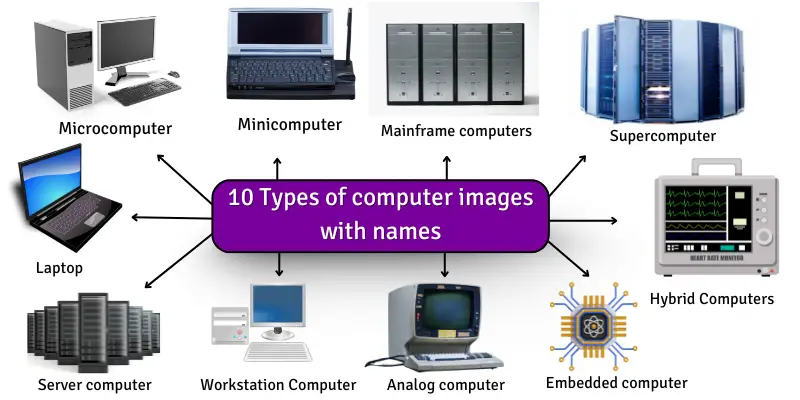
Different Types of Computers
Computers are classified based on size, performance, and purpose. From small personal devices to massive supercomputers, each type serves unique functions across homes, offices, industries, and research. Understanding these types helps in selecting the right computer for work, study, or specialized applications.
Microcomputers (Personal Computers)
Microcomputers are compact devices ideal for home, school, or office use. Examples include desktops and laptops.
Characteristics:
- Small and portable
- Affordable
- User-friendly
Uses:
- Homework and study
- Internet browsing
- Gaming

Minicomputers
Minicomputers are medium-sized, more powerful than microcomputers, supporting multiple users simultaneously. Examples: PDP-11, Data General Nova.
Characteristics:
- Moderate size and cost
- Multi-user support
Uses:
- Factories
- Businesses
- Hospitals

Mainframe Computers
Mainframes are large, powerful machines capable of handling thousands of tasks at once. Examples: IBM Z-series.
Characteristics:
- Multi-user support
- Large and costly
Uses:
- Banks
- Airports
- Government databases

Supercomputers
Supercomputers are the most powerful, handling complex calculations at incredible speeds. Examples: Summit.
Characteristics:
- Extremely fast and powerful
- Large and expensive
Uses:
- Weather forecasting
- Medical research
- Engineering simulations

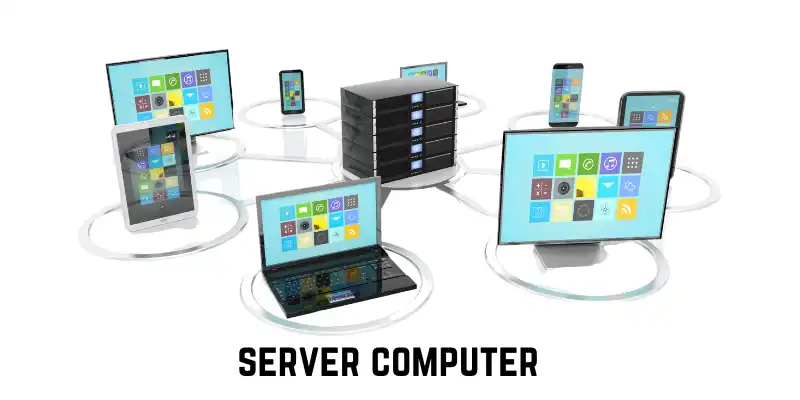
Server Computers
Servers store, manage, and share data with multiple users. Examples: Dell PowerEdge, HP ProLiant.
Characteristics:
- Powerful with large storage
- Multi-user support
Uses:
- Websites and cloud services
- Business data management
- Email hosting

Embedded Computers
Embedded computers are small systems integrated into devices for specific tasks.
Characteristics:
- Tiny and low power
- Dedicated functionality
Uses:
- Cars (engine, brakes)
- Home appliances
- Mobile devices
Workstation Computers
Workstations are high-performance computers for specialized tasks. Examples: Apple Mac Pro, Dell Precision.
Characteristics:
- Fast with high memory
- Advanced graphics
Uses:
- 3D modeling and design
- Video editing
- Scientific research

Laptops
Portable personal computers suitable for work and entertainment. Examples: HP Spectre, Dell Inspiron.
Characteristics:
- Portable and battery-powered
- Built-in keyboard
Uses:
- Typing and office work
- Watching videos
- Internet browsing

Analog Computers
Analog computers process data using physical measurements. Examples: thermometers, speedometers.
Characteristics:
- Continuous data processing
- Fast for specific tasks
Uses:
- Measuring temperature and speed
- Controlling machinery

Digital Computers
Digital computers process information using numbers (0 and 1). Examples: laptops, smartphones.
Characteristics:
- Fast and data-storing
- Accurate numerical processing
Uses:
- Gaming
- Writing and content creation
- Internet browsing

Hybrid Computers
Hybrid computers combine features of digital and analog systems. Example: hospital patient monitors.
Characteristics:
- Handles both digital and analog data
- Fast and versatile
Uses:
- Patient monitoring
- Space research
- Weather forecasting

Types of Computers (Quick Overview Table)
Here is a quick overview of the main types of computers, their key features, and real-life examples.
| Type of Computer | Size | Power | Example |
| Microcomputer | Small | Low–Medium | PC, Laptop |
| Minicomputer | Medium | Medium | PDP-11, Data General Nova |
| Mainframe Computer | Very Large | Very High | Banks, Airports |
| Supercomputer | Huge | Highest | Weather, Space Research |
| Server Computer | Large | High | Dell PowerEdge, HP ProLiant |
| Embedded Computer | Tiny | Low | Car Engine, Microwave |
| Laptop | Small | Medium | HP Spectre, Dell Inspiron |
| Analog Computer | Varies | Low–Medium | Speedometer, Thermometer |
| Digital Computer | Small–Large | Medium–High | PC, Smartphone |
| Hybrid Computer | Medium-Large | High | Hospital Patient Monitor |
Which Computer is Best? (Quick Reference)
Here is a quick reference to help you choose the best type of computer for different users and purposes.
| User / Purpose | Best Type of Computer | Reason |
| Students | Microcomputer / Laptop | Portable, easy to use, affordable, and can run educational software. |
| Small Office / Business | Minicomputer / Server | Can handle multiple users and store company data efficiently. |
| Banks / Airports / Govt | Mainframe Computer | Very powerful and secure for processing large amounts of data. |
| Scientific Research / Space | Supercomputer / Hybrid | Extremely fast and accurate for complex calculations and simulations. |
| Professional / Designers | Workstation Computer | High-performance and advanced graphics, suitable for design and video editing. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of computers?
The main types include microcomputers, minicomputers, mainframes, supercomputers, servers, embedded computers, workstations, laptops, analog, digital, and hybrid computers. Each type serves specific tasks depending on size, power, and purpose.
What is a microcomputer?
A microcomputer, like a desktop or laptop, is a small, affordable, and user-friendly computer ideal for home, school, and office use.
How does a mainframe differ from a supercomputer?
Mainframes handle multiple users and large-scale data processing simultaneously, while supercomputers perform extremely fast and complex calculations for scientific and engineering tasks.
What are embedded computers used for?
Embedded computers are tiny systems built into devices to perform specific functions, such as controlling car engines, home appliances, or mobile devices.
Which computer is best for businesses?
Servers and minicomputers are ideal for businesses, as they can store data, support multiple users, and manage applications efficiently.
What is the difference between digital and analog computers?
Digital computers use numbers (0 and 1) for data processing, while analog computers use physical measurements for continuous data calculations.
What are hybrid computers used for?
Hybrid computers combine digital and analog functions and are commonly used in patient monitoring, space research, and weather forecasting.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of computers is essential for choosing the right device for personal, educational, or professional use. From compact microcomputers and laptops to powerful mainframes and supercomputers, each type has unique features, capabilities, and applications. Servers, workstations, and embedded systems serve specialized roles in business, industry, and daily life, while hybrid, analog, and digital computers offer versatile solutions for complex tasks.
