The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of a computer, responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations that drive every operation. Understanding the different types of CPUs is essential for choosing the right processor for your needs, whether for gaming, professional work, or everyday computing.
CPUs vary in architecture, cores, clock speed, and power efficiency, influencing performance and capability. From single-core and multi-core processors to specialized chips like ARM and x86, each type serves unique purposes. Learning about Types of CPU helps users, students, and tech enthusiasts make informed decisions and optimize system performance.
Read More: Types of Headphones: Choosing the Best Option for Your Lifestyle
What Are the Types of CPU?
The CPU, often called the “brain” of a computer, comes in various types depending on its design and purpose. Some CPUs are built for general computing, powering desktops and laptops, while others are optimized for specialized tasks, such as mobile devices, servers, or supercomputers. Each type differs in architecture, cores, clock speed, and efficiency, affecting performance for specific applications.
Understanding these CPU types helps users, tech enthusiasts, and professionals choose the right processor for their needs, whether it’s for everyday use, gaming, or high-performance computing tasks.
Different Types of CPU
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brain of a computer, responsible for executing instructions and managing tasks. CPUs vary in design, purpose, and performance. Understanding the different types helps users choose the right processor for everyday use, gaming, or high-performance computing.
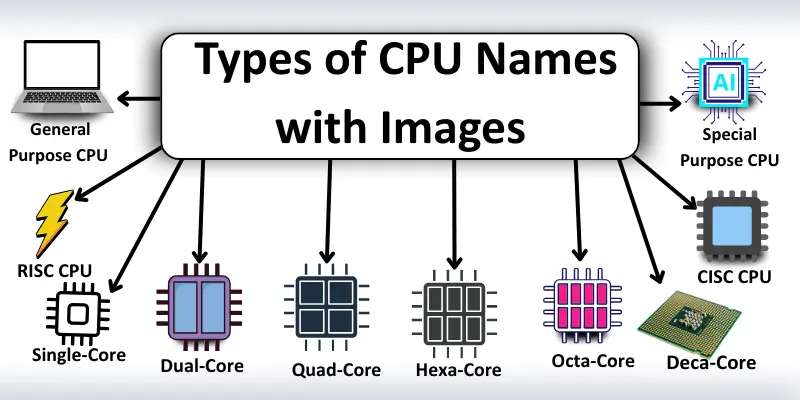
General-Purpose CPU
A general-purpose CPU handles multiple tasks simultaneously and is found in desktops, laptops, and servers. It’s designed for versatile computing rather than a single specialized function.
Characteristics:
- Uses standard instructions for programs
- Control unit guides execution
- Works with memory and cache for faster performance
- Compatible with Windows, Linux, macOS
Examples:
- Desktop: Intel Core i3, i5, i7; AMD Ryzen
- Mobile: ARM processors in smartphones and tablets
Special-Purpose CPU
A special-purpose CPU is designed for one specific task, offering speed and efficiency in that function. Common in smart devices, cars, and industrial machines.
Characteristics:
- Optimized for a specific task
- Excels at graphics, AI, or signal processing
- Trades general use for performance
Examples:
- Digital Signal Processor (DSP)
- Neural Processing Unit (NPU)
CISC CPU (Complex Instruction Set Computer)
CISC CPUs handle multiple instructions per cycle, ideal for complex computing tasks in desktops and laptops.
Characteristics:
- Performs more operations per instruction
- Reduces the number of steps for tasks
- Works efficiently for general-purpose applications
- Saves memory with compact instructions
Examples: Intel Core i5, AMD Ryzen 5
RISC CPU (Reduced Instruction Set Computer)
RISC CPUs focus on simple instructions executed very quickly, suitable for mobile devices and embedded systems.
Characteristics:
- Executes simple instructions step by step
- High efficiency and speed
- Lower energy consumption
- Simple architecture, easy to design
Examples: Qualcomm Snapdragon, NVIDIA Jetson
Single-Core CPU
Has one core, handling one task at a time. Common in old laptops and basic computers.
Characteristics:
- Efficient for small tasks
- Low power consumption
- Simple design and easy maintenance
Examples: Intel 80486, AMD K5
Dual-Core CPU
Contains two cores, capable of running two tasks simultaneously. Suitable for mid-range laptops and desktops.
Characteristics:
- Handles small to medium tasks efficiently
- Supports multitasking and light gaming
- Moderate power usage
Examples: Intel Core 2 Duo, AMD Athlon X2
Quad-Core CPU
With four cores, it can run four tasks simultaneously. Found in modern laptops, desktops, and some gaming PCs.
Characteristics:
- Ideal for multitasking and heavy software
- Faster than single- or dual-core CPUs
- Smooth performance for videos and browsing
Examples: Intel Core i5 (Quad-Core), AMD Ryzen 3 (Quad-Core)
Hexa-Core CPU
Has six cores, providing faster performance for high-demand applications and multitasking.
Characteristics:
- Handles multitasking smoothly
- Good for video editing, heavy software, and multitasking
- Consumes more power than quad-core CPUs
Examples: Intel Core i7 (Hexa-Core), AMD Ryzen 5 (Hexa-Core)
Octa-Core CPU
Contains eight cores, perfect for high-end laptops, desktops, and gaming PCs.
Characteristics:
- Smooth multitasking without lag
- Excellent for video editing, streaming, and 3D applications
- Higher power consumption than hexa-core CPUs
Examples: Intel Core i9 (Octa-Core), AMD Ryzen 7 (Octa-Core)
Deca-Core CPU
With ten cores, it is ideal for advanced desktops, servers, and professional workstations requiring extreme performance.
Characteristics:
- Handles many heavy tasks simultaneously
- Perfect for 3D rendering, video editing, and high-end gaming
- Higher power usage than octa-core CPUs
Examples: Intel Xeon (Deca-Core), AMD Ryzen Threadripper 10-Core
This rewrite keeps all key information, makes it easy to scan, and is perfect for SEO-optimized articles or blogs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a CPU and why is it important?
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brain of a computer, responsible for executing instructions and managing tasks.
What is the difference between general-purpose and special-purpose CPUs?
General-purpose CPUs handle multiple tasks for everyday computing, while special-purpose CPUs are optimized for a single, specific function like AI or graphics.
What are CISC and RISC CPUs?
CISC CPUs handle complex instructions efficiently, while RISC CPUs focus on executing simple instructions quickly with lower power consumption.
How do single-core and multi-core CPUs differ?
Single-core CPUs handle one task at a time, whereas multi-core CPUs (dual, quad, hexa, octa, deca) can perform multiple tasks simultaneously, improving speed and multitasking.
Which CPU is best for gaming and high-performance computing?
Multi-core CPUs such as hexa-core, octa-core, or deca-core are ideal for gaming, video editing, and resource-intensive applications.
What CPUs are commonly used in mobile devices?
Mobile devices typically use ARM-based processors or RISC CPUs, designed for energy efficiency and fast performance.
How do I choose the right CPU for my computer?
Consider your usage needs: general-purpose CPUs for everyday tasks, multi-core CPUs for gaming or heavy software, and special-purpose CPUs for specific applications.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of CPUs is essential for choosing the right processor for your computing needs. From single-core and multi-core processors to special-purpose CPUs like DSPs and NPUs, each type offers unique advantages in speed, efficiency, and performance. General-purpose CPUs power everyday desktops and laptops, while high-core CPUs handle gaming, video editing, and demanding applications.
