The first hard drive, launched in 1956, stored just 5 MB of data a fraction of today’s capacity. Modern hard drives can hold terabytes of information, safeguarding everything from photos and videos to crucial documents. As a core component of any computer, the hard drive ensures your data remains secure and easily accessible whenever needed.
Over the decades, advancements in storage technology have transformed hard drives from bulky, limited devices into efficient, high-capacity solutions essential for personal and professional use. Reliable storage allows seamless computing, backing up memories, projects, and vital information without compromise.
Read More: Software in Age of Digital Progress
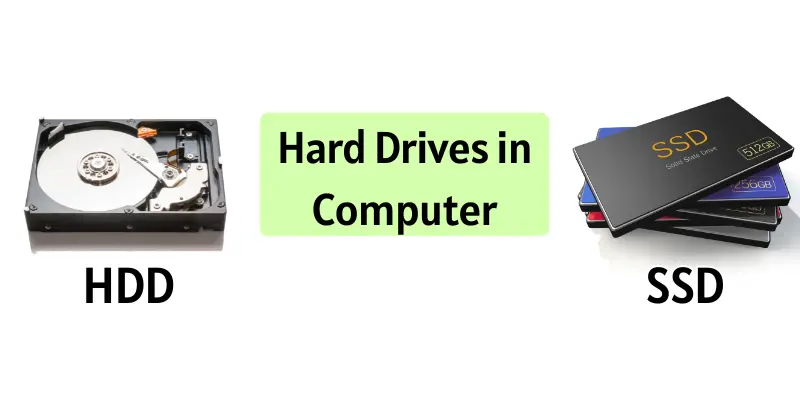
What is a Hard Drive?
A hard drive is a computer device that stores all your data, including files, photos, videos, and programs. It ensures your information remains safe and accessible even after the computer is turned off. Hard drives come mainly in two types: HDD and SSD, allowing quick storage and retrieval of data.
Types of Hard Drives
Hard drives vary in speed, storage, and cost:
- HDD (Hard Disk Drive): Uses spinning disks to store data; affordable but slower.
- SSD (Solid State Drive): Uses memory chips; fast, reliable, and more expensive.
- Hybrid Drive (SSHD): Combines HDD and SSD for both speed and storage.
BHow Hard Drives Work
- HDD: Contains spinning disks (platters) and a read/write head that moves to access data. Faster spinning means quicker access.
- SSD: Uses memory chips with no moving parts, providing instant file access.
Key Components
- HDD: Platters, read/write head, spindle.
- SSD: NAND flash memory chips.
- Controller: Manages reading and writing.
- Casing: Protects the components.
Think of a hard drive like a library: your files are books, and the drive helps you locate them whenever needed.
Capacity and Speed
- HDD: 500 GB–16 TB; 5,400–10,000 RPM. Offers more storage at a lower cost.
- SSD: 120 GB–2 TB; 400–3,500 MB/s. Faster but smaller and pricier.
In summary, HDDs provide high storage for less money, while SSDs deliver superior speed and performance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hard Drives
Hard drives are essential for storing computer data, offering both benefits and limitations.
Advantages
- Store large amounts of data easily.
- Simple to install and use.
- SSDs deliver extremely fast performance.
- HDDs offer cost-effective large storage.
- Retain data even when the computer is off.
Disadvantages
- HDDs are slower than SSDs.
- Susceptible to damage from drops or impacts.
- Limited lifespan over time.
- SSDs are more expensive than HDDs.
- Data loss can occur from viruses or disk errors.
Fun Facts About Hard Drives
Hard drives are full of surprises. Here are some interesting facts:
- The first hard drive, created in 1956, stored just 5 MB of data.
- Modern hard drives can hold up to 16 TB of data.
- SSDs have no moving parts, making them quieter and more durable than HDDs.
- Hard drives aren’t just for computers—they’re also used in servers, gaming consoles, and cameras.
- Some data centers use thousands of hard drives to store millions of files for the internet.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a hard drive?
A hard drive is a device that stores all your computer’s data, including files, programs, photos, and videos. It keeps information safe even when the computer is turned off.
What are the main types of hard drives?
The main types are:
- HDD (Hard Disk Drive): Uses spinning disks; affordable and high storage.
- SSD (Solid State Drive): Uses memory chips; faster, more reliable, but costlier.
- Hybrid Drive (SSHD): Combines HDD and SSD features for both speed and storage.
How does a hard drive work?
HDDs use spinning platters and a read/write head to access data. SSDs use memory chips, allowing instant data retrieval without moving parts.
How much data can a hard drive store?
HDDs typically range from 500 GB to 16 TB, while SSDs range from 120 GB to 2 TB.
What are the advantages of a hard drive?
Hard drives offer large storage, easy installation, data safety, cost-effectiveness (HDDs), and high speed (SSDs).
What are the disadvantages of a hard drive?
HDDs are slower, can be damaged physically, and have limited lifespan. SSDs are more expensive, and all drives risk data loss due to viruses or disk errors.
Where are hard drives used?
Besides computers, hard drives are used in servers, gaming consoles, cameras, and large data centers.
How do I choose between HDD and SSD?
Choose HDD for large, cost-effective storage and SSD for faster performance and durability.
Conclusion
Hard drives are the backbone of modern computing, storing all your files, programs, and data safely. Whether you choose an HDD for its large, cost-effective storage or an SSD for speed and durability, understanding their types, functions, and limitations helps you make the right choice. With evolving technology, hard drives continue to play a vital role in computers, servers, gaming, and data centers, keeping our digital world organized and accessible.
