Understanding the difference between HTTP vs HTTPS is crucial for anyone navigating the digital world. HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) and HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) are protocols that enable communication between web browsers and servers. While HTTP provides the basic framework for data transfer, HTTPS adds a layer of security through encryption, protecting sensitive information such as passwords, payment details, and personal data.
Websites using HTTPS are more trusted by users and favored by search engines, making security a key factor for online credibility and SEO performance. This guide explores the core differences between HTTP and HTTPS, highlighting their impact on website security, user trust, and overall online experience.
Read More: HTTP vs HTTPS: Key Differences Explained
10 Key Differences Between HTTP vs HTTPS
HTTP and HTTPS are protocols that govern how websites transmit data to your device. Understanding their differences is essential for online security, privacy, and website credibility.
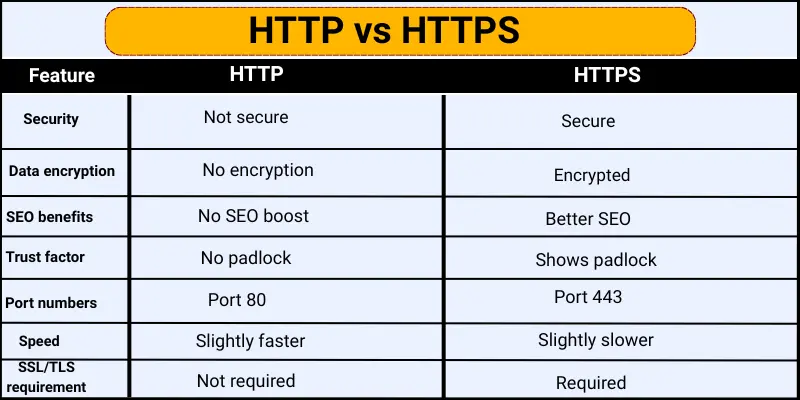
- Security
- Data Encryption
- SEO Benefits
- Trust Factor
- Port Numbers
- Speed
- User Privacy
- SSL/TLS Requirement
- Website Credibility
- Vulnerability
10 Key Differences Between HTTP and HTTPS
Security
Security determines how safe your data is online.
- HTTP: Data is sent in plain text, making it vulnerable to hackers. Not suitable for passwords or personal details.
- HTTPS: Encrypts data, protecting it from hackers. Ideal for online banking, shopping, and private communications.
Data Encryption
Encryption converts information into a secret code during transfer.
- HTTP: No encryption; data can be easily intercepted.
- HTTPS: Encrypts data so only the intended website can read it.
SEO Benefits
Search engines favor secure websites.
- HTTP: No ranking advantage; may get lower visibility.
- HTTPS: Preferred by Google, helping sites rank higher and attract more traffic.
Trust Factor
Trust encourages users to interact safely.
- HTTP: Lacks security indicators; users may feel unsafe.
- HTTPS: Displays a padlock icon, increasing user confidence and trust.
Port Numbers
Ports determine how data is sent over the internet.
- HTTP: Uses port 80; no extra security.
- HTTPS: Uses port 443; supports encrypted connections.
Speed
Website loading speed affects user experience.
- HTTP: Slightly faster as it doesn’t encrypt data.
- HTTPS: Slightly slower due to encryption, but modern tech makes it negligible.
User Privacy
Protecting personal information is essential.
- HTTP: Offers no privacy; data can be seen by others.
- HTTPS: Encrypts data, safeguarding users’ personal information.
SSL/TLS Requirement
SSL/TLS creates a secure link between users and websites.
- HTTP: Doesn’t use SSL/TLS; connection is unsafe.
- HTTPS: Requires SSL/TLS, ensuring secure data transfer.
Website Credibility
Credibility impacts user trust and professionalism.
- HTTP: Appears less professional; may reduce trust.
- HTTPS: Shows a padlock and secure connection, enhancing credibility.
Vulnerability
Vulnerability measures susceptibility to attacks.
- HTTP: Easily targeted; data is unprotected.
- HTTPS: Harder to hack due to encryption; reduces security risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between HTTP and HTTPS?
HTTP transfers data in plain text, making it less secure. HTTPS encrypts data using SSL/TLS, protecting user information and enhancing website trust.
Why is HTTPS important for websites?
HTTPS secures sensitive information, improves SEO rankings, builds user trust, and reduces the risk of cyberattacks.
How does HTTPS affect SEO?
Search engines like Google prioritize HTTPS websites in search results, helping them rank higher and attract more visitors.
Is HTTPS slower than HTTP?
HTTPS may be slightly slower due to encryption, but modern technology makes the difference almost unnoticeable.
Can hackers steal data from HTTP websites?
Yes. HTTP sends data without encryption, making it vulnerable to interception and theft by hackers.
What is the SSL/TLS certificate, and why is it needed?
SSL/TLS encrypts data between the browser and server. HTTPS requires it to ensure safe communication and protect user privacy.
How can I tell if a website is HTTPS?
Look for a padlock icon in the browser’s address bar and “https://” at the beginning of the URL. This indicates a secure connection.
Conclusion
HTTPS is the modern standard for secure websites, offering encryption, user privacy, and increased trust. While HTTP may still exist for basic browsing, it lacks protection and exposes data to hackers. Choosing HTTPS not only safeguards sensitive information but also improves SEO rankings, enhances website credibility, and builds user confidence. For businesses and individuals alike, adopting HTTPS is essential for a safe, reliable, and professional online presence. Always prioritize secure connections to protect both your website and your users.
